|
DIGITAL HEALTH AND AI |
“Digital Health in the fight against disease”He has 30 years of experience in eHealth and connected health, medical imaging, biosignal analysis, intelligent systems and explainable AI, and more recently in mHealth interventions based on X Reality applications. He has been involved in numerous projects in these areas funded by EU and other bodies, with a total funding managed exceeding 20 million euros. He has published 150 journal publications, 265 conference papers, 3 monographs, 30 chapters in books and co-editor of 4 edited volumes, 22 journal special issues and 20 conference proceedings. He was the Technical Leader of the EU project funded under the Emergency Support Instrument Action for Cyprus to implement the EU Digital Covid Certificate Platform for the issuance of the corresponding certificates for vaccination, recovery and laboratory testing (eudcc.gov.cy which has been used by more than 1 million users). He is also leading the “Deployment of Generic Cross Border eHealth Services in Cyprus”, an EU funded project under the Recovery and Resilience Plan for Cyprus, where 25-member states participate under the Health and Digital Executive Agency (HaDEA) and eHealth Digital Service Infrastructure. He is a Member of the European Academy of Sciences and Arts, Fellow of IEEE, IET, International Academy of Medical and Biomedical Engineering (IAMBE) and European Alliance for Medical & Biological Engineering & Science (EAMBES). Professor Constantinos S. Pattichis Director of Biomedical Engineering Research Center, Department of Computer Science @ University of Cyprus & Leader of HealthXR Group, CYENS Centre of Excellence pattichi-AT-ucy.ac.cy; (+357) 22 892697
Integrated explainable AI inMedical ImagingOngoing work on explainable AI (XAI) focuses on the development of an explainable machine learning framework based on argumentation that supports flexible reasoning in the face of unknown and incomplete information together with a natural form of explainability functionality.
An integrated modular multi-feature/multi-classifier diagnostic system, including normalization, de-speckle filtering, plaque segmentation, texture feature extraction, and classification was developed for differentiating between asymptomatic and symptomatic plaques in ultrasound imaging of the carotid for the assessment of the risk of stroke. This system was used in several cardiovascular clinics in North America, Europe, and Asia.
An XAI model was developed for Multiple Sclerosis (MS) disease evolution based on texture features extracted from brain MRI lesions. The findings indicated that the proposed model can predict the clinical conditions of MS disease with high accuracy and provide transparent and understandable explanations with high fidelity.
Radiomic features based on texture analysis from both the entorhinal cortex and the hippocampus were extracted from normal controls (NC), mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and AD subjects. Texture analysis evaluates statistical properties of the image intensities which might represent changes in MRI image pixel intensity due to the pathophysiology of a disease. The importance of XAI modelling was demonstrated in the assessment of AD towards earlier diagnosis and better management of disease progression. |
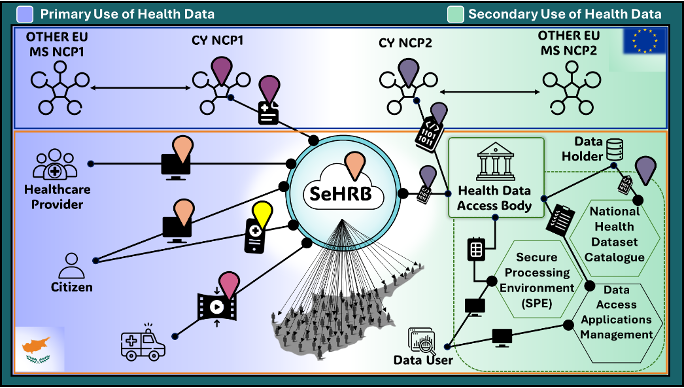
Advancing citizen-centered healthcare via:Digital HealthThe following digital health projects are carried out in collaboration with the National eHealth Authority of Cyprus enabling Cyprus to be an integral part of ”MyHealth@EU” in the context of the European Health Data Space (EHDS) for both primary and secondary use of data.
A prototype national Electronic Health Record (EHR) platform was developed using the HL7 FHIR interoperability standard in combination with terminologies widely adopted by the clinical community such as the SNOMED CT. The health-related data of this EHR are separated into three main sections, being the “Medical History”, the “Clinical Examination” and the “Laboratory results”. Business requirements include the Patient Summary as defined by the guidelines of the eHealth network and the International Patient Summary which are used as the base for all the sections of the EHR.
This project supports Cyprus to be part of “MyHealth@EU” a secure peer-to-peer Member States network allowing the exchange of medical
Texture analysis of endoscopy images in gynaecological cancer was proposed enabling the differentiation between normal and abnormal endometrium tissue. Given that there is no standardized methodology for the interpretation of endoscopy images our protocol is being discussed for consideration by the European Society for Gynaecological Endosopy (ESGE). Patient empowerment viaVR Interventions
The results of this study provide further evidence that Virtual Reality (VR) can play a significant role in the improvement of physical and emotional health of people with dementia. VR can successfully be deployed in hospital environments to alleviate behavioral and psychological symptoms of in-patients with dementia and improve their quality of life.
Work is carried out closely with cancer patients and medical personnel to co-design an intelligent personalized portable VR application for pain management based on symptoms management and fatigue and Health-Related Quality of Life.
|
documentation no matter where you are in EU through the eHealth Digital Service Infrastructure (eHDSI) for the exchange of: Patient Summary, ePrescriptions, eDispensing, to be followed by Medical Imaging and Lab Reports and Hospital Discharge Letters. Twenty-five EU countries will be connected by 2025 and Cyprus is expected to GO-LIVE by 2024.
The MYeHealthAppCY is connected to the eHealth4U and cross-border platform covering secure access of citizen’s medical data, including also teleconsultation.
The Cyprus national health data access body (HDAB) will be implemented as envisaged in the proposed EHDS Regulation, enabling Cyprus connectivity infrastructure to foster secondary exchange of health data in EU.
Research work focuses on mHealth diagnostically driven efficient video compression algorithms using video coding standards including H.264/AVC, H.265/HEVC, and more recently H.266/VVC. The system was demonstrated successfully in ambulance, emergency scenery video scenario as well as in low-delay tele-ultrasound scenarios.
Enhancing learning in Medical EducationThe integration of VR through 360° videos in healthcare curricula enhances learning by providing immersive, realistic scenarios for medical training. For instance, the CoViRR project focuses on surgical excision of skin lesions, allowing students to practice in a safe, repeatable environment. This approach improves understanding, confidence, and competence in clinical skills.
The CEPEH initiative explored the development and application of chatbots in medical education, providing virtual patient interactions and course assistance, showing promise in improving large-scale learning scenarios, though further research is needed to fully establish their efficacy and integration into medical curricula.
|
|
SELECTED GRANTS
|
SELECTED PUBLICATIONS
|